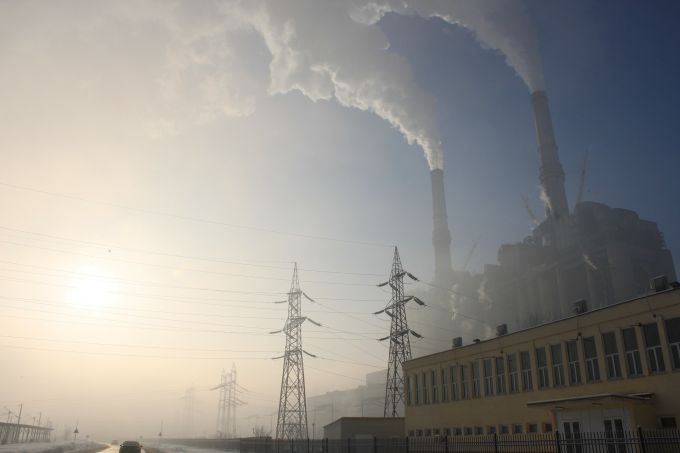
The Canadian oil and gas industry could be emitting methane at rates 25 to 50 percent higher than official estimates, according to new research.
A study published Tuesday in the journal Environmental Science & Technology compared measurements taken from airplane surveys of fossil fuel infrastructure in Alberta to emissions reported by industry—which is only required to report intentional emissions from flaring, and not estimate leaked emissions—and other figures.
“Our first reaction was ‘Oh my goodness, this is a really big deal,'” study author Matthew Johnson told the Guardian. “If we thought it was bad, it’s worse.” Alberta, Canada’s top fossil fuel-producing province, has set a goal of reducing methane emissions 45 percent by 2025—a target researchers say could be severely compromised by the study’s findings.
As reported by the Guardian:
“Canadian advocacy group Environmental Defence described the findings as alarming. ‘The methane gas currently being wasted would supply almost all the natural gas needs of Alberta, and is worth $530m per year,’ Dale Marshall of the organisation said in a statement. ‘This represents an economic cost for governments in the form of lost royalties and taxes, and for industry in terms of revenue.’
Marshall pointed to the readily available solutions for controlling leaks and intentional releases of methane gas, portraying them as some of lowest cost strategies available to reduce carbon emissions.”
Source: ecowatch.com