People who deny that humans are wreaking havoc on the planet’s life-support systems astound me. When confronted with the obvious damage we’re doing to the biosphere—from climate change to water and air pollution to swirling plastic patches in the oceans—some dismiss the reality or employ logical fallacies to discredit the messengers.
It’s one thing to argue over solutions, but to reject the need for them is suicidal. And to claim people can’t talk about fossil fuels and climate change because they use fossil fuel–derived products, such as plastic keyboards, is nonsensical.
There’s no denying that oil, coal and gas are tremendously useful. They hold super-concentrated energy from the sun and are used to make a variety of products, from medicines to lubricants to plastics. The problems aren’t the resources but our profligate use of them. Using them more wisely is a start. In many cases, we also have alternatives.
Burning oil, coal and gas to propel inefficient automobiles and generate electricity illustrates the problem. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), about 14 to 30 percent of a gasoline-powered car’s fuel is used to propel the vehicle. That energy is mostly moving a tonne of car, which often holds one 80-kilogram person. That’s a lot of fuel and energy to transport one or two people.
Looked at this way, even electric or hybrid personal vehicles aren’t terribly efficient, but they at least pollute less than gas-powered vehicles—and the EPA notes 74 to 94 percent of an electric car’s energy goes to moving the vehicle and its passengers. Energy-efficient or electric vehicles are moving in the right direction, but public transit and active transport such as cycling and walking are better alternatives.
Fossil fuel power plants are also inefficient. Only about a third of the power generated reaches consumers. More is lost through wasteful household or business use. A lot of energy is also required to extract, process and transport fuels to power plants. Because of the many methods of generating and supplying electricity with renewable sources such as solar, wind and geothermal, it’s tough to put exact numbers on efficiency, but far less power is wasted. Because the energy sources are inexhaustible and don’t produce emissions, waste isn’t as big a concern as with fossil fuels—although it’s still important.
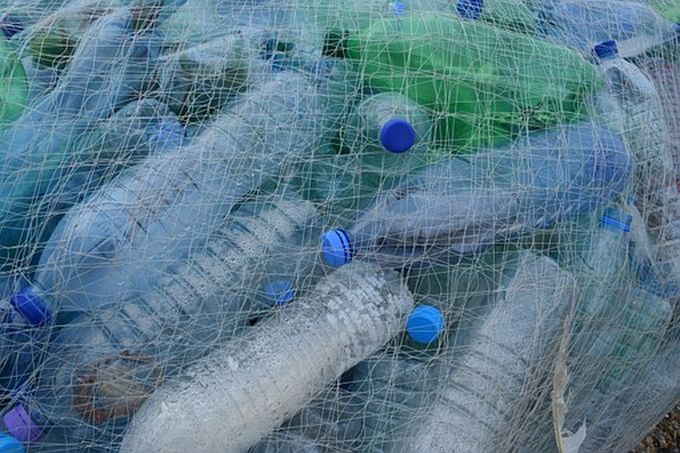
Most plastics are also made from oil—which presents another set of problems. As with fuels, people started making plastics from oil because it was inexpensive, plentiful and easy for corporations to exploit and sell. Our consume-and-profit economic system meant automakers once designed cars not to be efficient but to burn more fuel than necessary. Likewise, manufacturers create far more plastic products than necessary. Many items don’t serve much purpose beyond making money. Sometimes the packaging is worth more than the contents!
It’s so bad that researchers from Australia’s University of Tasmania and the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds recently found 18 tonnes of plastic garbage—239 items per square meter—scattered across a small South Pacific island 5,000 kilometers from the nearest human occupation. Scientists have also found massive, swirling patches of plastic in the North and South Pacific oceans, each holding around 400,000 plastic particles per square kilometer. University of Tasmania researcher Jennifer Lavers said plastic in the oceans could be as great a threat as climate change. “You put carbon dioxide into the atmosphere or plastic in the oceans and both will stick around,” she told New Scientist.
As with fossil fuels, the first step to addressing the problem is to substantially reduce plastics usage. There are also alternatives. To begin, we should recycle everything already produced. Plastics can also be made from renewable resources, such as hemp or any fast-growing plant that contains cellulose. In fact, plastics were once commonly made from animal products such as horn and tusks, but when those became expensive, people started using plants, switching to oil products when that became more profitable.
We can and must cut down on fossil fuels and plastics. We also have alternatives, and ways to prevent plastics from ending up in the oceans. Those who look away and pretend we don’t have a problem are only slowing solutions and accelerating our self-destruction.
Source: ecowatch.com