
Scotland is seeking to dramatically cut its reliance on fossil fuels for cars, energy and homes after setting a radical target to cut total climate emissions by 66% within 15 years.
In one of the world’s most ambitious climate strategies, ministers in Edinburgh have unveiled far tougher targets to increase the use of ultra-low-carbon cars, green electricity and green home heating by 2032.
The Scottish government has set the far higher target after its original goal of cutting Scotland’s emissions by 42% by 2020 was met six years early – partly because climate change has seen winters which are warmer than normal, cutting emissions for home heating.
The new strategy, which is expected to cost up to £3bn a year to implement and is closely linked to a new renewable energy programme due to be published this month, will call for:
• 40% of all new cars and vans sold in Scotland to be ultra-low-emission by 2032, with 50% of Scotland’s buses to be low-carbon.
• A totally carbon-free electricity sector based entirely on renewable energy sources by 2032, when Scotland’s last nuclear power station will close.
• Four out of five of Scotland’s 2m homes to be heated using low-carbon technologies.
• The repairing of 250,000 hectares of degraded peatlands, which store a total of 1.7 gigatonnes of CO2 in Scotland.
• At least 30% of Scotland’s vital publicly owned ferry fleet to be low-carbon, powered by hybrid engines.
Enriched by a vast £727bn sovereign wealth fund built up from its North Sea oil and gas industries, Norway has set Europe’s most ambitious emissions reduction target so far, committing itself to become carbon neutral by 2030 – two decades earlier than planned.
But that target, a cut equal to 53m tonnes of carbon equivalent, will rely very heavily on carbon trading: paying other countries to cut their emissions more deeply or buying carbon credits from industries which are cutting emissions.
Scotland’s 66% target, on the other hand, will be based on real-terms cuts in domestic emissions, although ministers admit there are serious policy and financial challenges raised by the UK’s decision to quit the EU. Nor does the strategy include Scotland’s substantial offshore oil and gas industry, or its oil exports, only covering onshore emissions.
The Scottish environment secretary, Roseanna Cunningham, told MSPs at Holyrood on Thursday that the proposals “represent a new level of ambition which will help maintain Scotland’s reputation as a climate leader within the international community”.
But Cunningham said that Scottish businesses, homeowners and commuters – whom ministers privately see as too reluctant to change their behaviour – now had to take a far greater share of the burden.
Until now, a large proportion of Scotland’s decline in CO2 emissions has been driven by the sharp shift to renewable energy from windfarms, an EU-wide move away from coal-powered energy, EU emissions trading and worldwide technical advances, particularly on car engine efficiency.
Scottish drivers will now be asked to quickly start taking up electrically powered or hybrid cars; homeowners will be encouraged to strip out gas-fired boilers at home and improve insulation; farmers will be asked to cut the methane and nitrogen climate gases, and Network Rail will be paid to electrify 35% of Scotland’s rail network.
Richard Dixon, chief executive of Friends of the Earth Scotland, said he applauded the government’s ambition, but it still overlooked substantial issues, particularly an economic strategy wedded to roads and aviation. The Scottish government wants to abolish air passenger duty to increase flying in a bid to stimulate growth.
“It paints a very good vision of what a low-carbon Scotland could look like in 2032,” he said. “But there are clearly areas where there has been resistance and policies either aren’t going far enough or aren’t credible.”
Ministers should put far greater stress on forcing motorists out of their cars and on to far more energy-efficient public transport or bicycles, Dixon said. Farmers should be forced to accept compulsory testing for overuse of climate-damaging fertilisers. There had to be far tougher standards on home energy efficiency.
The 2032 target will include legally binding annual targets first agreed by the Scottish parliament in 2009. Officials estimate that hitting that goal will cost annually about 2% of Scotland’s GDP, which is worth about £147bn a year.
More offshore windfarms and marine energy plants will be needed, as will hundreds of thousands of electrical car charging points, alongside the cost of more than 1m new home heating systems.
But ministers believe that improving air quality, cutting fuel poverty, increasing home insulation, and reducing road accidents through less use of cars will save public money by cutting NHS spending and early deaths, as well as boosting economic output.
They worry about the impact the UK’s departure from the EU will have on continuing pan-European funding and investment in the low-carbon economy, and the EU emissions trading regime, which plays a large part in reducing emissions.
The current EU emissions targets are a 40% cut by 2030, while the UK government’s goal is to cut emissions by 50% by 2025, with an 80% target set for 2050.
Officials have previously acknowledged that policies and industries under the Scottish government’s control cover about 30% of Scotland’s overall emissions; the remainder is influenced or controlled at UK and EU level, and international industries.
Source: theguardian.com




 Christian Zinglersen, the Deputy Permanent Secretary at the Danish Ministry of Energy, Utilities and Climate, was named the first Head of Secretariat for the new Clean Energy Ministerial Secretariat, established at the International Energy Agency (IEA).
Christian Zinglersen, the Deputy Permanent Secretary at the Danish Ministry of Energy, Utilities and Climate, was named the first Head of Secretariat for the new Clean Energy Ministerial Secretariat, established at the International Energy Agency (IEA).






 Addressing the World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland, United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres yesterday called for a new generation of partnerships with the business community to limit the impact of climate change and to reduce poverty.
Addressing the World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland, United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres yesterday called for a new generation of partnerships with the business community to limit the impact of climate change and to reduce poverty.
 Last week ISWA launched its latest publication “Waste Management Outlook for Mountain Regions”.This new publication is a cooperation with United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), International Environmental Technology Centre (IETC) and GRID-Arendal.
Last week ISWA launched its latest publication “Waste Management Outlook for Mountain Regions”.This new publication is a cooperation with United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), International Environmental Technology Centre (IETC) and GRID-Arendal.
 Dong Energy will present its oil and gas exploration and production activities as “discontinuing operations” in its financial statements for 2016.
Dong Energy will present its oil and gas exploration and production activities as “discontinuing operations” in its financial statements for 2016.




 Plant for the waste water treatment in the Carlsberg beer factory in Čelarevo opened in 2010 in the presence of the top state officials. This brewery is among the first in Serbia which presented this kind of facility. They wanted to emphasize that they care about the broader community and the environment.
Plant for the waste water treatment in the Carlsberg beer factory in Čelarevo opened in 2010 in the presence of the top state officials. This brewery is among the first in Serbia which presented this kind of facility. They wanted to emphasize that they care about the broader community and the environment.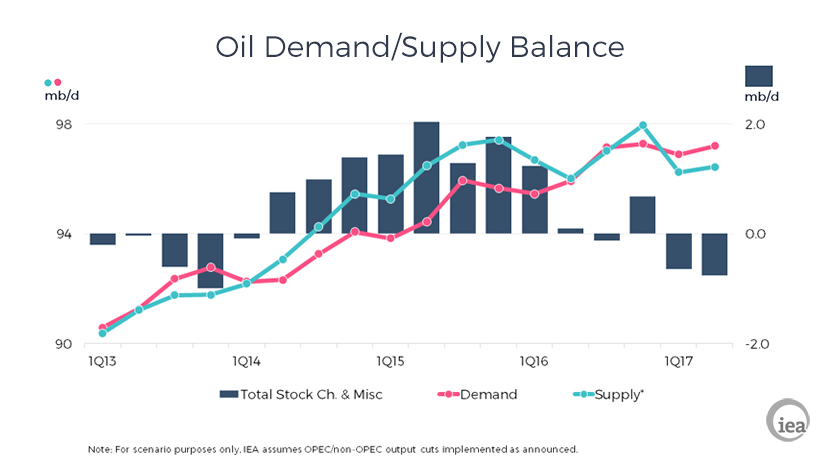
 The output cuts announced by OPEC and eleven non-OPEC producers have entered their probation period and it is far too soon to see what level of compliance has been achieved. The coming weeks will provide more clarity and in the meantime developments elsewhere in the oil supply/demand balance are very intriguing. Once again we have revised upwards our estimate for global oil demand growth in 2016: we now see growth at 1.5 mb/d, with most of the revision contributed by stronger European demand, mainly in LPG and diesel. Europe has seen two years of year-on-year growth following nine straight years of flat or declining demand.
The output cuts announced by OPEC and eleven non-OPEC producers have entered their probation period and it is far too soon to see what level of compliance has been achieved. The coming weeks will provide more clarity and in the meantime developments elsewhere in the oil supply/demand balance are very intriguing. Once again we have revised upwards our estimate for global oil demand growth in 2016: we now see growth at 1.5 mb/d, with most of the revision contributed by stronger European demand, mainly in LPG and diesel. Europe has seen two years of year-on-year growth following nine straight years of flat or declining demand.

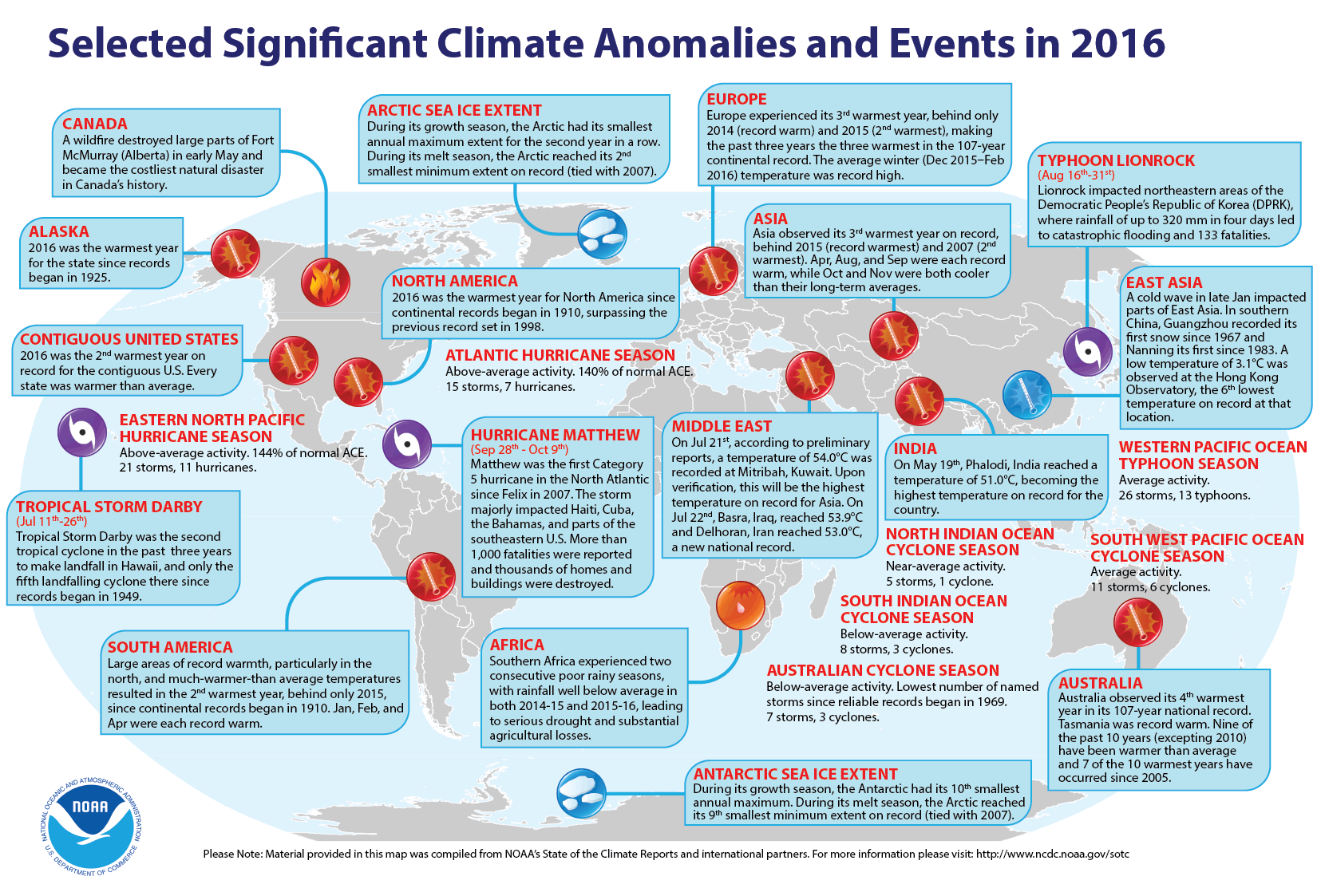
 The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) yesterday announced that the year 2016 has been the hottest year on record, surpassing the exceptionally high temperatures of 2015, according to a consolidated analysis.
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) yesterday announced that the year 2016 has been the hottest year on record, surpassing the exceptionally high temperatures of 2015, according to a consolidated analysis.
 The OPEC Monthly Oil Market Report covers major issues affecting the world oil market and provides an outlook for crude oil market developments for the coming year. The report provides a detailed analysis of key developments impacting oil market trends in world oil demand, supply as well as the oil market balance. Please find the Report
The OPEC Monthly Oil Market Report covers major issues affecting the world oil market and provides an outlook for crude oil market developments for the coming year. The report provides a detailed analysis of key developments impacting oil market trends in world oil demand, supply as well as the oil market balance. Please find the Report 