Groupe Renault today announced Renault MOBILITY, which has been in its pilot phase since June 2016 at the La Défense site (France), in partnership with the Schumacher group Renault Bellini dealership. With this service, Renault will offer the public and companies its vehicles under a car sharing scheme, with both electric and combustion engine vehicles (ZOE, Captur, Clio). Renault brand aims to develop its solutions in urban and rural areas through its network of partners, to offer a truly local service.
“With Renault MOBILITY, Renault offers a Renault brand vehicle or other, made easily accessible and available at any time. The aim is to meet all travel needs, from individuals to whole fleets, with flexible and adaptable solutions at the best price,” said Christophe Chevreton, Renault France director of the new mobility project.
In addition to individual use, a company’s employee may then use a Renault brand vehicle or other, under the carsharing scheme both for his business and private travel. The cost will be borne by the company for all business use and billed to the employee for his private use. This service has been in place at Plessis-Robinson (France) since the end of 2015.
A new player in the carsharing market in France, Renault MOBILITY uses the technological solutions provided by RCI Mobility, a subsidiary of RCI Bank and Services. The system will be launched officially for the Paris Motor Show, which will take place in October.
Source: media.renault.com








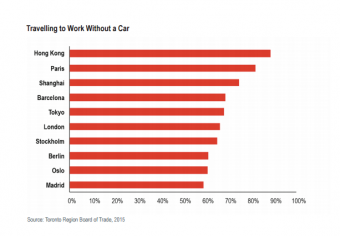 Nearly 90% of Hong Kong’s residents commute without using a car, while more than 80% of Parisians travel to work on foot, by bike or using public transport, according to research outlined in JLL’s Benchmarking the Future of World Cities report.
Nearly 90% of Hong Kong’s residents commute without using a car, while more than 80% of Parisians travel to work on foot, by bike or using public transport, according to research outlined in JLL’s Benchmarking the Future of World Cities report.
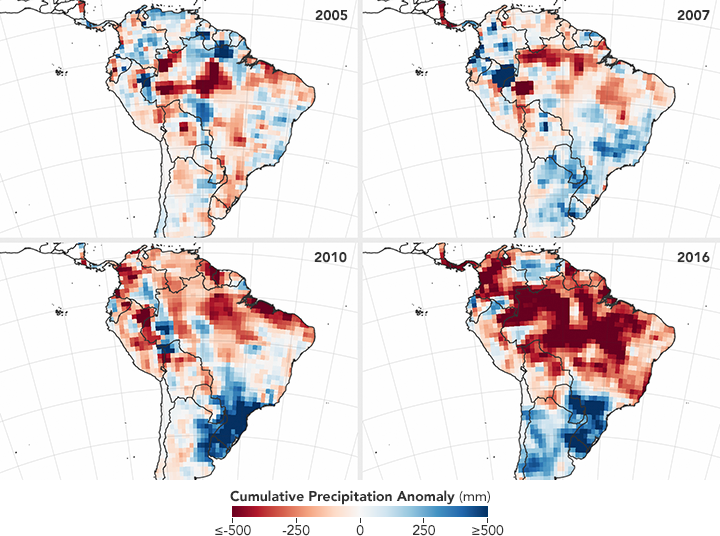
 The basis of socially responsible functioning of each company is the fact that it becomes aware of the importance and necessity of its own impact on improving general social conditions and the environment in which it operates. This is the reason why the energy efficiency has become a permanent commitment and strategic scheme of the Atlantic Group to reduce the impact on the environment through the rationalization of energy and water consumption, decreasing of waste and increasing of waste separation, generally in all our processes.
The basis of socially responsible functioning of each company is the fact that it becomes aware of the importance and necessity of its own impact on improving general social conditions and the environment in which it operates. This is the reason why the energy efficiency has become a permanent commitment and strategic scheme of the Atlantic Group to reduce the impact on the environment through the rationalization of energy and water consumption, decreasing of waste and increasing of waste separation, generally in all our processes.