The current climate situation requires reduced emissions of harmful gases to stop the increase in the average global temperature above 1.5 degrees Celsius compared to the pre-industrial level. To find a straightforward solution to the challenges we are facing, we need to go back to the beginning and understand the cause that led us to the problem we are fighting against.
What is the carbon footprint?
Every human activity leaves a carbon footprint. Put simply, the total amount of greenhouse gas emissions produced directly or indirectly by people, organizations, events and companies is a carbon footprint. Its quantity measures our impact on the environment and climate change. Carbon footprint represents the sum of all emissions of carbon dioxide and other gases that retain heat in the atmosphere, causing global warming, and which humans cause by their actions over a certain period. As a guideline for the fight against these adverse effects, the European Union has set an ambitious goal – carbon neutrality by 2050. To reach the set goal, the Fit for 55 set of regulations and measures was adopted to accomplish the goal of a 55 per cent net reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2030.
Everyone can reduce their carbon footprint by changing their lifestyle and consumption habits, such as reducing the use of cars that run on fossil fuel, using renewable energy sources, consuming more sustainable products, and making smarter use of living and working space. And that’s just a small part of the changes we can implement. Companies, institutions, governments and large organizations are the ones that should make the greatest effort but also show others by example how positive changes can occur. That is why many of them strive to do responsible business, which puts environmental protection and the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions in the foreground.
IN FOCUS:
- WASTEWATER TREATMENT AND PRESERVATION OF FRESH WATER SOURCES
- CHARGE&GO IS EXPANDING THE CHARGING NETWORK
- WWF IS LOOKING FOR CREATIVE PROJECT IDEAS FROM THE CIVIL SECTOR
Responsible business as a choice
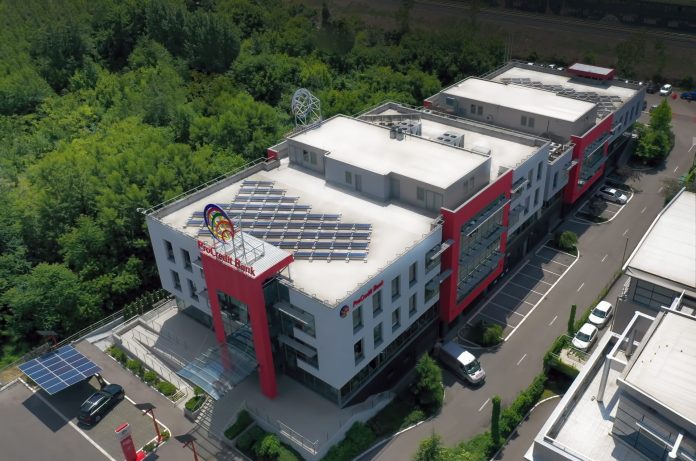
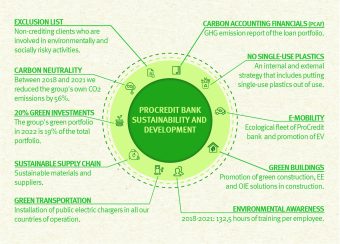
ProCredit Bank gives a good example of this practice. The Bank contributed at the Group level by reducing its share of carbon dioxide by 56 per cent between 2018 and 2021. This was achieved by using solar energy, monitoring electricity and heat consumption, banning single-use plastics in business premises, and purchasing electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles, with the goal that all vehicles in the Bank’s fleet will emit zero CO2 by the end of 2022. The Bank has been doing business responsibly for decades because it takes responsibility for assessing the environmental impact of not only its own but also the activities of its clients on the environment and society. Thanks to dedicated work, ProCredit Bank is recognized as a green transition leader in Serbia.
ProCredit Bank’s every activity must be verified as sustainable, which is why the Bank works on planning and optimizing procedures to save resources almost daily. The fact that all the Bank’s operations must not have an impact on the environment, which is why the Bank will never lend to someone whose activities negatively affect the environment, regardless of the profitability the business brings, demonstrates just how committed the Bank is to achieving the set goals. Thanks to a careful and prudent approach to credit risk analysis and avoiding making compromises for the sake of profit, ProCredit Bank has a stable and strong loan portfolio. The constant education of employees about sustainable and responsible business and environmental protection ensures additional stability and security. The Bank works every day to transfer everything they apply to their clients and train them how to make their business sustainable.
Prepared by: Milica Radičević
Read the story in the new issue of the Energy portal Magazine RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS.