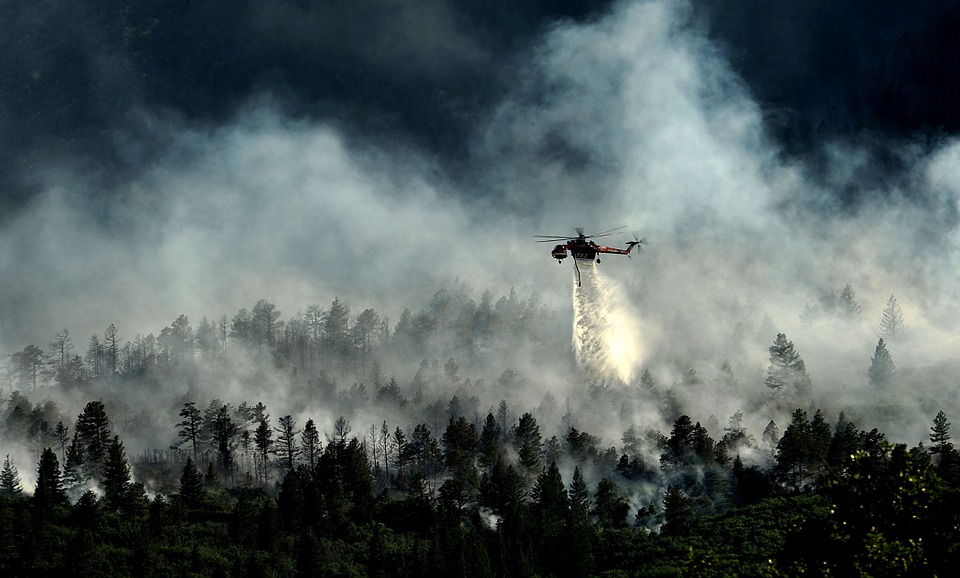
Until recently, wildfires were considered seasonal, mostly local phenomena, but over time, they have become a global crisis rapidly spreading under the influence of various changes. In recent decades, especially over the past 15 years, a record number of wildfires with devastating consequences have been recorded, severely impacting forest ecosystems, human lives, and biodiversity.
Human activity is often the cause of wildfires—from unattended campfires or discarded cigarette butts to the intentional burning of vegetation for urban development and agricultural expansion. Natural causes, such as lightning strikes, make up a much smaller share, but can be extremely dangerous when combined with drought, high temperatures, and strong winds, which accelerate the spread of fire. Additionally, due to urbanization and construction, people are increasingly settling and building on the edges of forests, increasing the risk of fires.
The most affected region in terms of wildfires is undoubtedly the western United States, which faces this problem between June and October, with the peak usually in August and September. However, even the beginning of 2025 brought terrifying scenes from Los Angeles. Canada is also among the countries most affected by the scale of wildfires, having lost several million hectares of forest to flames in 2023. The year 2024 fared no better, with hundreds of active fires at the same time. The situation is similar in the Southern Hemisphere, where Australia is most frequently impacted between December and March.
Artificial Intelligence as a Solution
In the search for new solutions, innovative projects are emerging, such as the SensoRy AI platform. This technology was developed by a young man from California, starting as a science fair project. Over time, it evolved into a system based on a combination of sensors for flame, smoke, and heat, along with infrared cameras and machine learning algorithms, which are now entering the testing phase in the field. Its goal is the early detection of natural hazards and fire alerts in high-risk areas. As soon as the sensor detects a potential fire source, it alerts local firefighting services, helping to prevent major wildfires.
IN FOCUS:
- Low Development of E-Mobility in Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Slovenian E-Mobility Solutions Conquering the World
- Farizon and the Future of Electric Commercial Vehicles
In addition, this could be a true ecological technology, as it doesn’t stop at fire detection but could also be used for identifying other types of pollution, including methane leaks or water contamination. Thanks to real-time data processing algorithms, the system could detect a problem even before visible signs appear.
Wildfires are no longer just a local issue; any delay in addressing the problem leads to even more severe consequences. Projects like this one, which are attuned to science and technological advancement, can prevent catastrophic outcomes and help preserve forests, which are vital for life on Earth.
Record Forest Loss by 2023
Statistics published by Global Forest Watch provide a deeper understanding of the scale of the problem. In 2020, the world had 3.68 billion hectares of natural forests, accounting for about 28 percent of total land area. By 2023, a loss of 23.9 million hectares of natural forest was recorded for various reasons.
When analyzing wildfires specifically, the statistics reveal that between 2001 and 2023, 138 million hectares of forest were lost—an area roughly 15 times the size of Serbia. In 2023, the largest recorded forest loss occurred when fire consumed 11.9 million hectares, representing 42 percent of all tree loss that year.
Problems are also reported in Mediterranean countries such as Greece, Italy, Spain, and Turkey, where fires are increasingly difficult to control due to heat waves and strong winds. According to the European Forest Fire Information System (EFFIS), between 300,000 and 600,000 hectares burn annually in the European Union, and in 2023, half a million hectares were lost to fires.
Serbia’s Situation Is Less Drastic Than in Other Parts of the World
From 2001 to 2023, Serbia lost an average of 154 hectares of forest annually due to fires, placing it at 94th on the Global Forest Watch ranking. While fires were responsible for just under 5 percent of tree loss in Serbia, experiences from other countries teach us that caution and preventive action are necessary to minimize the risk of fire outbreaks.
Every hectare of forest lost reduces nature’s ability to absorb carbon dioxide, regulate temperature, and provide habitats for numerous species. That is why it is essential to recognize the seriousness of this issue and contribute to its resolution—through responsible forest management, fire prevention, and raising awareness of the importance of protecting natural resources. We can only reduce risks and preserve forests for future generations through joint efforts.
Prepared by Milica Vučković
Read the story in the new issue of the Energy portal Magazine SUSTAINABLE MOBILITY