Last year was marked by record-high methane emissions from the energy sector. However, the end of the year brought the United Nations Conference on Climate Change 2023 (COP28) and the pledges that set an ambitious target for reducing these emissions.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) has published the Global Methane Tracker, the first comprehensive assessment of global methane emissions since the end of COP28. The research showed that the production and use of fossil fuels led to almost 120 million tonnes of emissions in 2023, which is more than the year before. Furthermore, another 10 million tonnes of methane emissions came from bioenergy.
10 countries alone were responsible for about 80 million tonnes of methane emissions from fossil fuels last year. The United States as the world’s largest producer of oil and gas, occupies first place, followed by Russia. In terms of coal, China takes the first place.
As stated, even if the existing pledges on reduced methane were to be fully implemented, the reduction, as per the Paris Agreement’s goal of 1.5°C, would not be achieved. The IEA estimates that in order to accomplish the aforementioned goal, it is necessary to reduce methane emissions from fossil fuels by 75 percent in this decade and with the current pledges, the reduction would be about 50 percent.
More:
- AIR QUALITY: COUNCIL AND PARLIAMENT STRIKE DEAL TO STRENGTHEN STANDARDS IN THE EU
- HOW CAN SATELLITES AND ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE REDUCE METHANE EMISSIONS?
- CLEAN TECHNOLOGIES REDUCED THE GROWTH OF GLOBAL CO2 EMISSIONS
Although 2023 saw record-high emissions, efforts to reduce these emissions are expected to grow in 2024 and beyond. This comes after 200 governments agreed at COP28 to significantly reduce methane emissions by 2030, as well as pledges from other Conference participants.
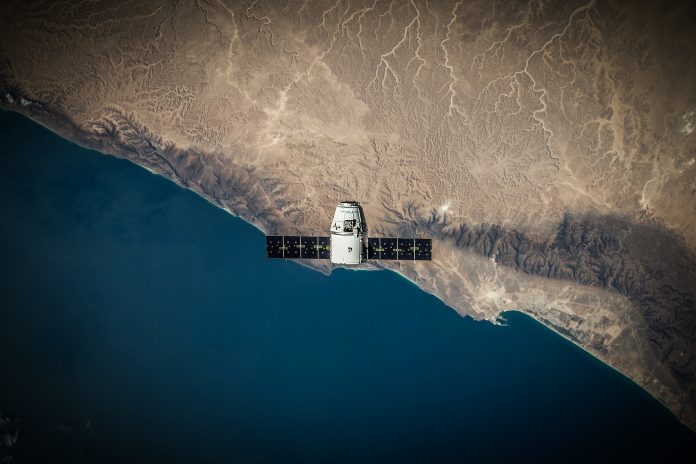
The IEA states that satellites play an important role in methane reduction, as they monitor global methane emissions and thus help identify and reduce them. The satellite that has been drawing attention lately is MethaneSAT, which thanks to the cooperation of Google and the Environmental Defense Fund, locates and measures emissions from oil and gas operations around the planet, more precisely than any satellite so far.
Google will make the data collected by the satellite available on the Google Earth Engine platform for environmental monitoring at the planetary level. This platform provides a wealth of geospatial data and tools for its analysis. Thus, users will be able to combine the data collected by the satellite with other data sets and analyze them.
Katarina Vuinac